Underwater archaeology

Science, studying the monuments of ancient civilizations, lost in the depths of the sea, is called in different ways: Aqua-archaeology, hydroarchaeology, underwater archaeology. But in all these definitions there is a word linking them together — archaeology. Given the place and circumstance of the birth of science, we prefer the name — archaeology of the sea. It is chosen because the main objects of research of this science are sunken cities, ships, people and the sea itself — the cradle of human civilization. The history of ancient society was closely linked with the sea at all stages of its development.
Underwater archaeology is an auxiliary discipline of archaeology concerned with the study of artifacts under water. Its history dates back to the early twentieth century, when Greek fishermen discovered the wreck of an ancient ship carrying statues.
Since the second quarter of the XX century underwater archaeology acquires the status of science. After the invention of aqualung by J.-Y. Cousteau studying the heritage of man under the water became more accessible and popular.
In the USSR, the pioneers were professors R. A. Orbeli, K. E. Grinevich, V. D. Blavatsky, G. A. Koshelenko..
Currently, there are about two dozen official underwater archaeological expeditions in Russia, under the General patronage Of the Institute of archaeology of the Russian Academy of Sciences, as well as a number of methodological centers: The Confederation of underwater activities of Russia; the Moscow underwater archaeological club; the voluntary center of underwater heritage at the Tolstoy Tula University.
Underwater archaeology is the historical subdiscipline by which underwater objects, artifacts, human settlement remains, and landscapes are studied. These studies should be considered within the broader context of marine archaeology, which studies human relationships with oceans, lakes and rivers and is complemented by marine archaeology, through which the history of ship construction and their use is studied. Underwater archaeological sites consist of debris (sunken ships or aircraft); remains of structures, litter or debris of the remains of human settlements that have subsequently been covered by water due to sea level rise or other phenomena. Very often they can contain, due to the lack of oxygen, materials that are not available on comparable objects on dry land.
Divers can be engage in amateur or professional underwater archaeology. There is still a lot of unknown in our world. There are enough objects hidden under the water to be explored for a generations of obsessives. These are lost cities, ancient vessels with "treasures", modern vessels with various values, victims of famous catastrophes. The sea allows objects to be preserved for many hundreds and even thousands of years.
The use of modern instruments for exploration and detection of archaeological sites at the bottom of the sea was dictated by the imperfection of the mechanical method of inspection and visual observations. Even the most experienced submariner cannot notice the increase in the relief of the seabed at 10-12 cm. Let us recall the difficulties that faced the divers, conducting work in muddy water. That's why the researchers decided to use the device, which is in service with the Navy of their countries. This device turned to be an echo sounder. But its application showed that the sound pulse, passing through the water column, is not completely reflected from the seabed, the nature of which (hardness, softness) also causes the errors of the device due to the" ground " reflections of sound. In addition, the sounder did not allow the object to be detected unless the vessel passed directly over it. And what if you need information about the stratigraphy of not only the monument, but also the layer that underlies it?
Search systems came to the assistance, which allowed to get an acoustic "photo" of the bottom. The resulting image allows you to identify the object, determine its geometry and state, dimensions. Having a binding of the received acoustic image of a bottom to geographical coordinates, it is possible to define easily coordinates of interesting objects. For the detection of archaeological objects in the soil of a bottom there are widely used:
- military archaeology
- ancient and medieval archaeology
- подводная археология и дайвинг
- treasure hunting and collecting
for search and classification (identification) of sunken objects, determination of coordinates and depth of sunken objects, creation of maps of sunken objects, etc.
| Acoustic image of the wooden frame of the ship, obtained using the SSS series Hydra |
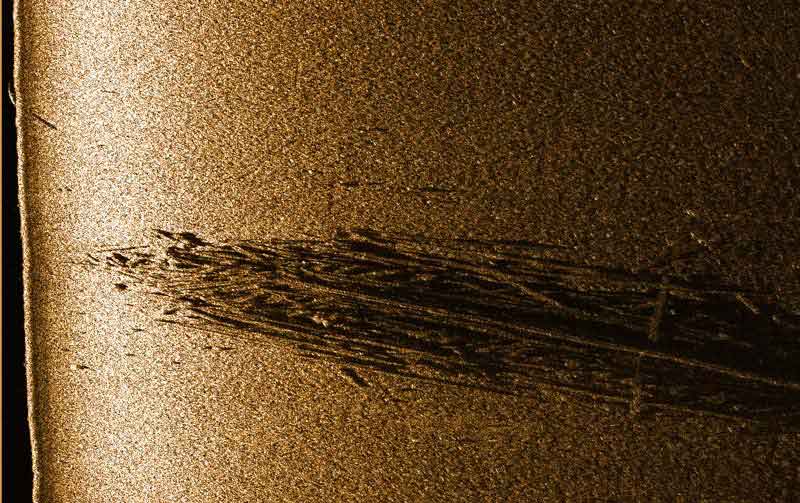 |
| Acoustic image of the remains of the wooden skeleton of the ship, obtained using SSS series Hydra (Baltic sea) |
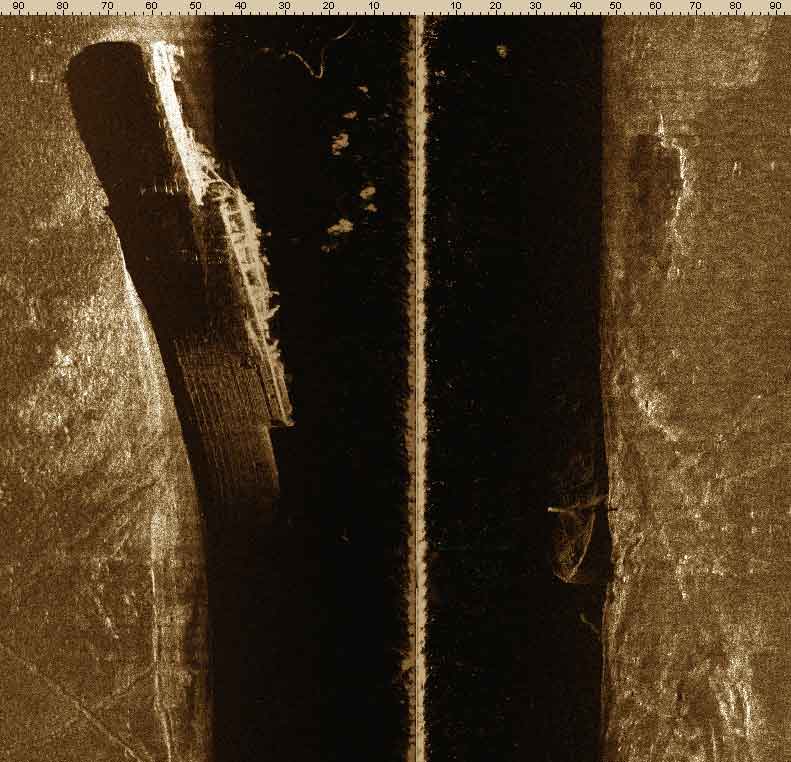 |
| Acoustic image of the sunken ship "Admiral Nakhimov", obtained using SSS series Hydra (Black sea) |
 |
| Acoustic image of the sunken ship "Rattling", obtained using SSS series Hydra |
 |
| Acoustic image of the sunken ship "New Russia", obtained with the help of SSS series Hydra |
 |
| Acoustic image of a world War II-Era aircraft obtained using the Hydra series SSS |
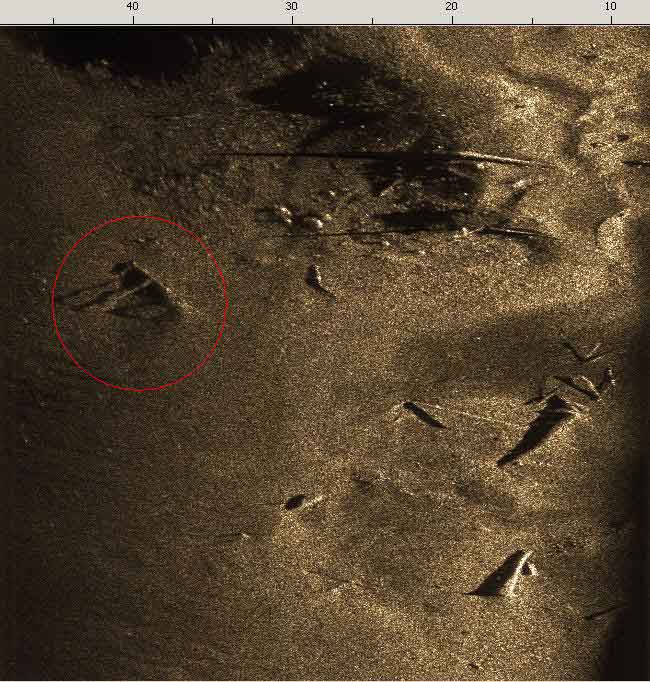 |
| Acoustic image of an anchor from a world War II ship obtained using the Hydra series SSS (Baltic sea) |
